Blockchain
Bitcoin (BTC) Layer 2 Revolution: The Role of Ordinals in Sparking Innovation

The introduction of Ordinals has ignited a surge of innovation within Bitcoin’s ecosystem, particularly through various Layer 2 implementations. These include a variety of rollup-based Layer 2s, anchored-chains, sidechains, state channels, liquidity pools, and Proof of Stake L2s, all aimed at enhancing Bitcoin’s scalability and functionality. By enabling off-chain transaction processing, these solutions increase transaction throughput and reduce fees, maintaining Bitcoin’s security while supporting complex applications. This wave of innovation bridges the gap between Bitcoin’s conservative “sound money, store of value” approach and the experimental, versatile world of Ethereum’s DeFi and Web3, ultimately expanding Bitcoin’s utility while paving the way for DeFi on Bitcoin.
Ordinals Have Opened the Pandora’s Box of Layer 2 Experimentation
The introduction of Ordinals within the Bitcoin ecosystem has indirectly sparked a wave of innovation, particularly regarding Layer 2 (L2) implementations. This includes a diverse array of solutions such as rollups, anchored-chains, sidechains, drivechain, ecash, state channels, liquidity pools, spiderchains, and even Proof of Stake and staking L2s. These advancements bring new features and capabilities, bridging the gap between Bitcoin’s conservative “sound money, store of value” philosophy and the more experimental and versatile world of Ethereum’s DeFi and Web3 ecosystems.
Drivechains, for example, are a notable Layer 2 solution proposed to enhance Bitcoin’s functionality without altering its core protocol. They allow for the creation of sidechains where altcoins can operate on Bitcoin, facilitating permissionless experimentation, new features, and improved scalability. This model eliminates inter-token competition and integrates successful altcoin innovations into Bitcoin, potentially making altcoins obsolete.
Rollups represent another critical innovation within Bitcoin’s Layer 2 landscape. These off-chain scaling solutions process transactions outside the main blockchain and then post summarised data back to Bitcoin’s Layer 1. This method enhances transaction throughput and reduces fees, addressing scalability issues. There are several types of rollups being explored, including optimistic rollups, which assume transactions are valid by default but can be disputed, and Zero Knowledge (ZK) rollups, which use cryptographic proofs to ensure transaction validity without revealing underlying data.
The development of other Layer 2 solutions like state channels, anchored-chains, and liquidity pools introduces additional functionalities to Bitcoin like smart contract capabilities and full Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) compatibility. State channels enable instant and low-cost transactions by allowing multiple transactions off-chain before recording the final state on-chain. Anchored-chains provide a way to secure additional blockchains using Bitcoin’s Proof of Work (PoW) consensus, while liquidity pools facilitate Decentralised Finance (DeFi) applications on Bitcoin by enabling users to pool their assets for lending, borrowing, and trading.
The advent of Ordinals has catalysed a significant expansion in Bitcoin’s Layer 2 ecosystem, bringing a variety of innovative solutions that enhance its functionality and scalability. L2.watch, a site which tracks Bitcoin L2 projects, currently tracks 85 different projects in the space, which are currently working on expanding Bitcoin’s L2 capabilities in one way or another. These advancements bridge the traditional gap between Bitcoin’s conservative monetary approach and the experimental DeFi and Web3 features prevalent in Ethereum. By incorporating solutions like sidechains, rollups, state channels, and liquidity pools, Bitcoin is poised to offer a more versatile and comprehensive platform while maintaining its core principles of security and decentralisation.
Love Them or Hate Them the Impact of Ordinals is Undeniable
Ordinals and the Ordinals protocol were released as a novel way to inscribe individual Satoshis, the smallest units of Bitcoin, with unique metadata, thereby creating Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) directly on the Bitcoin blockchain. This innovative approach leveraged Bitcoin’s Taproot and Segwit upgrades to store data within transaction scripts, marking a significant departure from Bitcoin’s traditional financial transaction focus. The Ordinals protocol enabled the creation of Bitcoin-native digital artefacts, known as Inscriptions, which sparked considerable interest and debate within the Bitcoin community about the potential for additional non-financial uses of the blockchain.
Following the release of Ordinals, community-led experimentation rapidly expanded the possibilities for Bitcoin-based tokenisation and digital assets. This experimentation led to the development of Stamps, which embed data into the Bitcoin blockchain in a more permanent manner than Ordinals, and BRC-20 tokens, which utilised JSON inscriptions to create basic token contracts. Further advancements brought ORC-20 tokens, offering more flexibility with a variable supply and efficient use of block space. These innovations highlighted the demand for a broader range of digital assets and functionalities within the Bitcoin ecosystem, laying the groundwork for even more sophisticated tokenisation protocols.
The culmination of these efforts came with the launch of Runes, a new fungible token protocol designed to coincide with Bitcoin’s recent halving on April 20th, 2024. Runes were introduced as a user-friendly, UTXO-based alternative to existing tokenisation schemes, addressing inefficiencies and reducing blockchain bloat. By integrating seamlessly with Bitcoin’s architecture, Runes minimised the creation of unnecessary outputs and enhanced the overall usability of Bitcoin for tokenisation. This launch marked a significant milestone in Bitcoin’s evolution, as it embraced a more diverse range of digital assets and functionalities.
The wave of innovation sparked by Ordinals and subsequent protocols has led to a surge of interest in bringing NFTs, DeFi, and Web3 applications to Bitcoin via an expanding Layer 2 ecosystem. This vibrant ecosystem now includes a variety of projects focused on Decentralised Exchanges (DEXs), Decentralised Autonomous Organizations (DAOs), and advanced programmability. The explosion of new projects and approaches is transforming Bitcoin from a conservative “store of value” into a versatile platform capable of supporting complex financial instruments and DApps. This shift is enhancing Bitcoin’s utility, making it a formidable competitor in the rapidly evolving world of DeFi and Web3 technologies.
Some of the Bitcoin L2s Driving Innovation in the Bitcoin Ecosystem
Alpen Layer
Alpen Layer, developed by Alpen Labs, is a scaling solution designed to enhance Bitcoin’s utility and accessibility by leveraging zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs). Founded on the principles of permissionless, programmable, and composable networks akin to the internet, Alpen Layer seeks to overcome Bitcoin’s fundamental obstacles of privacy, programmability, and scalability while preserving its simplicity and security. By utilising ZKPs, Alpen Layer enables private, verifiable computations and transactions, facilitating the creation of advanced financial systems directly on the Bitcoin blockchain. This includes flexible wallets, BTC-collateralized stablecoins, and DeFI applications, all secured by Bitcoin’s crypto-economic trust. Alpen Layer’s vision aligns with expanding global financial access and individual agency, providing a powerful, scalable, and private infrastructure for the next generation of Bitcoin-based financial systems.
Bitlayer
Bitlayer is a cutting-edge Layer 2 solution for Bitcoin that integrates 100% EVM compatibility, allowing applications and developers from the Ethereum ecosystem to migrate seamlessly to Bitcoin without significant changes. Utilising Bitcoin’s security through BitVM, it ensures a trustless two-way peg combining Discreet Log Contracts (DLC) and BitVM, surpassing traditional multisig models. Bitlayer’s roadmap outlines progressive enhancements, from a PoS sidechain with multisig in its first mainnet version, evolving to a rollup-equivalent model, and finally achieving full Layer 1 verification with BitVM by mid-2025. This compatibility extends to existing Bitcoin wallets, such as Metamask and Unisat, facilitating user interaction and enabling developers to deploy smart contracts and projects on the Bitlayer network effortlessly.
Build On Bitcoin (BOB)
Build On Bitcoin (BOB) is a hybrid Layer 2 solution that merges the security of Bitcoin with the versatility of Ethereum, enabling developers familiar with the EVM to build on Bitcoin seamlessly. By combining Bitcoin’s proof-of-work security with best-in-class EVM tooling, BOB offers an efficient and secure environment for DApps. It connects to both Bitcoin and Ethereum ecosystems, leveraging dual liquidity to support DeFi mass adoption. The platform provides extensive developer resources, including a developer suite, SDK, and infrastructure tools, facilitating rapid development and deployment. BOB’s roadmap includes phases for enhancing its rollup model, aiming to integrate advanced technologies like BitVM and potential future ZK-Rollups.
Botanix Labs
Botanix Labs aims to transform Bitcoin into a fully programmable layer for the future of finance by developing the first decentralised EVM-equivalent Layer 2 on Bitcoin. Leveraging Bitcoin’s PoW for base settlement and decentralisation, Botanix integrates a PoS consensus model using the Spiderchain, a network of decentralised multisigs secured by a randomised subset of participants. This approach enables Bitcoin to maintain its unparalleled security while introducing the versatility of Ethereum’s EVM. Botanix Labs addresses Bitcoin’s current limitations in decentralised application development by creating a platform where developers can build decentralised exchanges, lending platforms, and more using Bitcoin as the native currency. The Spiderchain securely holds staked bitcoin in multisig wallets, ensuring the safety of funds through a system of checks and balances. Ultimately, Botanix envisions a hybrid system that combines the strengths of Bitcoin and Ethereum, fostering a robust ecosystem for DeFi, NFTs, and other decentralised applications on Bitcoin.
Lightec
Lightec is a group focused on advancing blockchain and web3 by incorporating zero-knowledge proof (ZKP) technology. Their goal is to develop a Layer 2 solution for Bitcoin, using ZKP to enhance privacy and data ownership for users, while promoting decentralised cooperation. They are currently working on two main projects: opZKP and zkBTC. The opZKP project seeks to add a new opcode (OP_CHECKZKP) to Bitcoin Script, allowing Bitcoin nodes to validate ZKP data as a condition for spending UTXO. This is akin to OP_CHECKSIG, but it verifies zero-knowledge proofs instead. This enhancement would enable the creation of smart contracts with off-chain computations that are verified on-chain. The zkBTC project aims to create a ZKP-based cross-chain bridge between Bitcoin and Ethereum, enabling users to utilise their Bitcoin in smart contracts on both networks without depending on centralised entities. This project will ensure secure and decentralised processes for minting and redeeming Bitcoin, thus broadening Bitcoin’s utility within the larger cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Mirror L2
Mirror L2 is a decentralised and secure Bitcoin staking protocol designed for Proof-of-Stake (POS) Layer 1 and Layer 2 projects. It employs an innovative Multi-Signature Group (MSG) mechanism that allows hundreds to thousands of nodes to collaboratively manage multi-signature wallets. Nodes are required to stake 1 mBTC and face penalties for any malicious behaviour, ensuring security and trustlessness. The protocol bridges staked BTC into mBTC at a 1:1 ratio, making it EVM-compatible and facilitating integration with EVM-based BTC L2s. This system allows mBTC to be used as native gas for POS L1/L2s, thus enhancing demand for BTC and promoting broader DApp development. Nodes are elected through a community voting process, which progressively increases node numbers to ensure robust decentralisation and security.
ZKBase
ZKBase is a project focused on enhancing both Bitcoin and Ethereum’s security and scalability through advanced Layer 2 solutions, utilising ZK protocols. Dedicated to improving the blockchain ecosystem, ZKBase offers a suite of products including ZKSwap, a decentralised Automated Market Maker (AMM) exchange, and ZKSpace, which encompasses ZKSwap, ZKSquare (a payment service), ZKSea (an NFT marketplace), and ZNS (a Layer 2 naming service). By employing ZK-Rollups technology, ZKBase aims to provide foundational support for various decentralised applications (dApps) and decentralised finance (DeFi) projects, facilitating cross-chain bridges and decentralised exchanges (DEXs) for enhanced connectivity between Bitcoin and Ethereum networks. The roadmap includes significant developments such as the introduction of a BTC ZKEVM solution, a decentralised BTC bridge, and extensive cross-chain functionality, positioning ZKBase as a pivotal player in the blockchain interoperability landscape.
SatoshiVM
SatoshiVM is a decentralised Bitcoin ZK Rollup Layer 2 solution that integrates the EVM ecosystem, allowing Bitcoin to issue assets and build applications using native BTC as gas. Designed with simplicity, SatoshiVM enables users and developers to interact and build on it just like Ethereum. Its architecture includes three layers: the Settlement Layer on Bitcoin for on-chain validation and verification, the Sequencing Layer for maintaining functionality and temporarily storing transactions and states, and the Proving Layer responsible for generating proofs and verifying transactions and states on Bitcoin. This setup leverages Bitcoin’s Taproot transactions to ensure the validity and security of SatoshiVM operations.
SatoshiSync
SatoshiSync is a chain-agnostic protocol designed to power Runes, Inscriptions, and Bitcoin Layer 2 solutions, facilitating seamless cross-chain interactions. It allows users to customise and deploy BRC20 tokens, bridge them to ERC20 or any EVM-compatible blockchain, and create markets with a single click through Uniswap. SatoshiSync offers a decentralised, no-code platform for creating open markets for Runes and Inscriptions, enabling users to track, discover, buy, and swap them easily. Its native token, SSNC, provides utilities like revenue capture from cross-chain fees, a deflationary supply mechanism, staking for rewards, and governance rights, empowering holders to participate in the platform’s development and earn rewards.
Image source: Shutterstock
Blockchain
Bitcoin (BTC) Price Crashes as Donald Trump’s Win Odds Dip
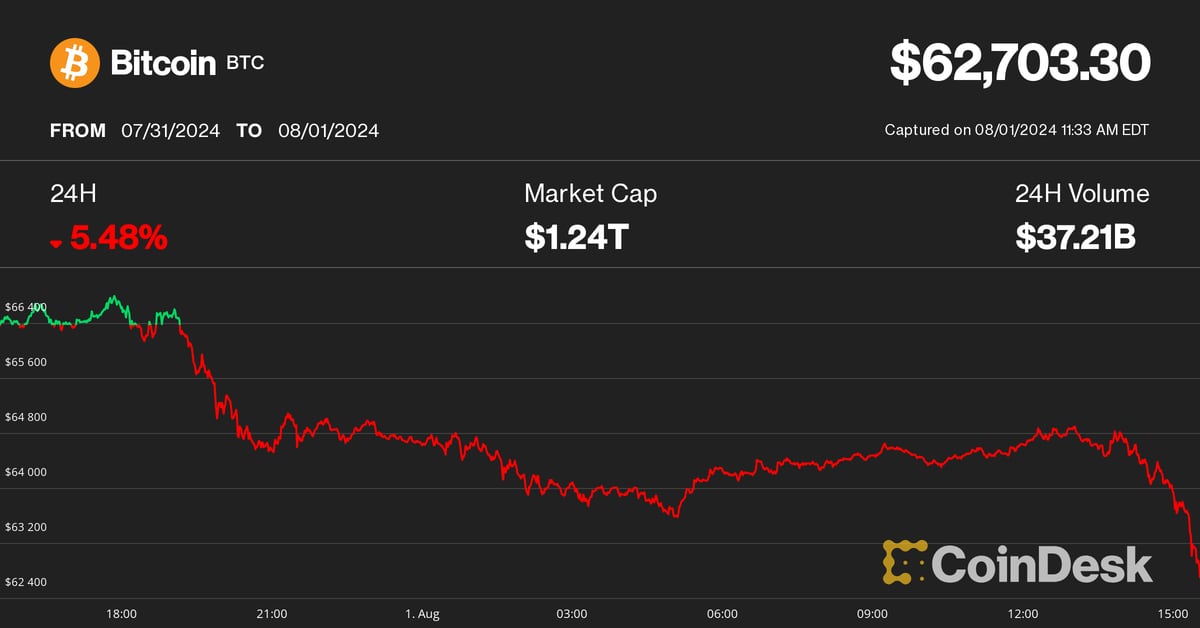
Markets received nominally good news on Thursday morning, with the US ISM manufacturing PMI for July falling much more than economists expected, sending interest rates to multi-month lows across the board. Additionally, initial jobless claims in the US jumped to their highest level in about a year. Taken together, the data adds to the sentiment that the US is on the verge of a cycle of monetary easing by the Federal Reserve, which is typically seen as bullish for risk assets, including bitcoin.
Blockchain
Terra Blockchain Reboots After Reentry Attack Leads to $4M Exploit

Please note that our Privacy Policy, terms of use, cookiesAND do not sell my personal information has been updated.
CoinDesk is a awarded press agency that deals with the cryptocurrency sector. Its journalists respect a rigorous set of editorial policiesIn November 2023, CoinDesk has been acquired from the Bullish group, owner of Bullisha regulated digital asset exchange. Bullish Group is majority owned by Block.one; both companies have interests in a variety of blockchain and digital asset businesses and significant digital asset holdings, including bitcoin. CoinDesk operates as an independent subsidiary with an editorial board to protect journalistic independence. CoinDesk employees, including journalists, are eligible to receive options in the Bullish group as part of their compensation.
Blockchain
$6.8M Stolen, ASTRO Collapses 60%
In the latest news in the blockchain industry, there has been a turn of events that has severely affected Terra and its users and investors, with the company losing $6.8 million. The attack, which exploited a reentry vulnerability in the network’s IBC hooks, raises questions about the security measures of the once celebrated blockchain protocol.
A web3 security company, Cyvers Alerts reported that the exploit occurred on July 31st and caused the company to lose 60 million ASTRO, 3.5 million USDC500,000 USDTand 2. 7 BitcoinThe flaw was discovered in April and allows cybercriminals to make payments non-stop by withdrawing money from the network.
Earth’s response
Subsequently, to the hack employed on the Terra blockchain, its official X platform declared the Suspension network operations for a few hours to apply the emergency measure. Finally in its sendTerra’s official account agreed, sharing that its operations are back online: the core transactions that make up the platform are now possible again.
However, the overall value of the various assets lost in the event was unclear.
Market Impact: ASTRO Crashes!
The hack had an immediate impact on the price of ASTRO, which dropped nearly 60% to $0.0206 following the network shutdown. This sharp decline highlights the vulnerability of token prices to security breaches and the resulting market volatility.
This incident is not the first time Terra has faced serious challenges. Earlier this year, the blockchain encountered significant problems that called into question its long-term viability. These repeated incidents underscore the need for stronger security measures to protect users’ assets and maintain trust in the network.
The recent Terra hack serves as a stark reminder of the ongoing security challenges in the blockchain space. As the platform works to regain stability, the broader crypto community will be watching closely.
Read also: Record Cryptocurrency Theft: Over $1 Billion Stolen in 2024
This is a major setback for Terra. How do you think this will impact the blockchain industry?
Blockchain
Luxembourg proposes updates to blockchain laws | Insights and resources

On July 24, 2024, the Ministry of Finance proposed Blockchain Bill IVwhich will provide greater flexibility and legal certainty for issuers using Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT). The bill will update three of Luxembourg’s financial laws, the Law of 6 April 2013 on dematerialised securitiesTHE Law of 5 April 1993 on the financial sector and the Law of 23 December 1998 establishing a financial sector supervisory commissionThis bill includes the additional option of a supervisory agent role and the inclusion of equity securities in dematerialized form.
DLT and Luxembourg
DLT is increasingly used in the financial and fund management sector in Luxembourg, offering numerous benefits and transforming various aspects of the industry.
Here are some examples:
- Digital Bonds: Luxembourg has seen multiple digital bond issuances via DLT. For example, the European Investment Bank has issued bonds that are registered, transferred and stored via DLT processes. These bonds are governed by Luxembourg law and registered on proprietary DLT platforms.
- Fund Administration: DLT can streamline fund administration processes, offering new opportunities and efficiencies for intermediaries, and can do the following:
- Automate capital calls and distributions using smart contracts,
- Simplify audits and ensure reporting accuracy through transparent and immutable transaction records.
- Warranty Management: Luxembourg-based DLT platforms allow clients to swap ownership of baskets of securities between different collateral pools at precise times.
- Tokenization: DLT is used to tokenize various assets, including real estate and luxury goods, by representing them in a tokenized and fractionalized format on the blockchain. This process can improve the liquidity and accessibility of traditionally illiquid assets.
- Tokenization of investment funds: DLT is being explored for the tokenization of investment funds, which can streamline the supply chain, reduce costs, and enable faster transactions. DLT can automate various elements of the supply chain, reducing the need for reconciliations between entities such as custodians, administrators, and investment managers.
- Issuance, settlement and payment platforms:Market participants are developing trusted networks using DLT technology to serve as a single source of shared truth among participants in financial instrument investment ecosystems.
- Legal framework: Luxembourg has adapted its legal framework to accommodate DLT, recognising the validity and enforceability of DLT-based financial instruments. This includes the following:
- Allow the use of DLT for the issuance of dematerialized securities,
- Recognize DLT for the circulation of securities,
- Enabling financial collateral arrangements on DLT financial instruments.
- Regulatory compliance: DLT can improve transparency in fund share ownership and regulatory compliance, providing fund managers with new opportunities for liquidity management and operational efficiency.
- Financial inclusion: By leveraging DLT, Luxembourg aims to promote greater financial inclusion and participation, potentially creating a more diverse and resilient financial system.
- Governance and ethics:The implementation of DLT can promote higher standards of governance and ethics, contributing to a more sustainable and responsible financial sector.
Luxembourg’s approach to DLT in finance and fund management is characterised by a principle of technology neutrality, recognising that innovative processes and technologies can contribute to improving financial services. This is exemplified by its commitment to creating a compatible legal and regulatory framework.
Short story
Luxembourg has already enacted three major blockchain-related laws, often referred to as Blockchain I, II and III.
Blockchain Law I (2019): This law, passed on March 1, 2019, was one of the first in the EU to recognize blockchain as equivalent to traditional transactions. It allowed the use of DLT for account registration, transfer, and materialization of securities.
Blockchain Law II (2021): Enacted on 22 January 2021, this law strengthened the Luxembourg legal framework on dematerialised securities. It recognised the possibility of using secure electronic registration mechanisms to issue such securities and expanded access for all credit institutions and investment firms.
Blockchain Act III (2023): Also known as Bill 8055, this is the most recent law in the blockchain field and was passed on March 14, 2023. This law has integrated the Luxembourg DLT framework in the following way:
- Update of the Act of 5 August 2005 on provisions relating to financial collateral to enable the use of electronic DLT as collateral on financial instruments registered in securities accounts,
- Implementation of EU Regulation 2022/858 on a pilot scheme for DLT-based market infrastructures (DLT Pilot Regulation),
- Redefining the notion of financial instruments in Law of 5 April 1993 on the financial sector and the Law of 30 May 2018 on financial instruments markets to align with the corresponding European regulations, including MiFID.
The Blockchain III Act strengthened the collateral rules for digital assets and aimed to increase legal certainty by allowing securities accounts on DLT to be pledged, while maintaining the efficient system of the 2005 Act on Financial Collateral Arrangements.
With the Blockchain IV bill, Luxembourg will build on the foundations laid by previous Blockchain laws and aims to consolidate Luxembourg’s position as a leading hub for financial innovation in Europe.
Blockchain Bill IV
The key provisions of the Blockchain IV bill include the following:
- Expanded scope: The bill expands the Luxembourg DLT legal framework to include equity securities in addition to debt securities. This expansion will allow the fund industry and transfer agents to use DLT to manage registers of shares and units, as well as to process fund shares.
- New role of the control agent: The bill introduces the role of a control agent as an alternative to the central account custodian for the issuance of dematerialised securities via DLT. This control agent can be an EU investment firm or a credit institution chosen by the issuer. This new role does not replace the current central account custodian, but, like all other roles, it must be notified to the Commission de Surveillance du Secteur Financier (CSSF), which is designated as the competent supervisory authority. The notification must be submitted two months after the control agent starts its activities.
- Responsibilities of the control agent: The control agent will manage the securities issuance account, verify the consistency between the securities issued and those registered on the DLT network, and supervise the chain of custody of the securities at the account holder and investor level.
- Simplified payment processesThe bill allows issuers to meet payment obligations under securities (such as interest, dividends or repayments) as soon as they have paid the relevant amounts to the paying agent, settlement agent or central account custodian.
- Simplified issuance and reconciliationThe bill simplifies the process of issuing, holding and reconciling dematerialized securities through DLT, eliminating the need for a central custodian to have a second level of custody and allowing securities to be credited directly to the accounts of investors or their delegates.
- Smart Contract Integration:The new processes can be executed using smart contracts with the assistance of the control agent, potentially increasing efficiency and reducing intermediation.
These changes are expected to bring several benefits to the Luxembourg financial sector, including:
- Fund Operations: Greater efficiency and reduced costs by leveraging DLT for the issuance and transfer of fund shares.
- Financial transactions: Greater transparency and security.
- Transparency of the regulatory environment: Increased attractiveness and competitiveness of the Luxembourg financial centre through greater legal clarity and flexibility for issuers and investors using DLT.
- Smart Contracts: Potential for automation of contractual terms, reduction of intermediaries and improvement of transaction traceability through smart contracts.
Blockchain Bill IV is part of Luxembourg’s ongoing strategy to develop a strong digital ecosystem as part of its economy and maintain its status as a leading hub for financial innovation. Luxembourg is positioning itself at the forefront of Europe’s growing digital financial landscape by constantly updating its regulatory framework.
Local regulations, such as Luxembourg law, complement European regulations by providing a more specific legal framework, adapted to local specificities. These local laws, together with European initiatives, aim to improve both the use and the security of projects involving new technologies. They help establish clear standards and promote consumer trust, while promoting innovation and ensuring better protection against potential risks associated with these emerging technologies. Check out our latest posts on these topics and, for more information on this law, blockchain technology and the tokenization mechanism, do not hesitate to contact us.
We are available to discuss any project related to digital finance, cryptocurrencies and disruptive technologies.
This informational piece, which may be considered advertising under the ethics rules of some jurisdictions, is provided with the understanding that it does not constitute the rendering of legal or other professional advice by Goodwin or its attorneys. Past results do not guarantee a similar outcome.
-

 Regulation12 months ago
Regulation12 months agoRipple CTO and Cardano founder clash over XRP’s regulatory challenges ⋆ ZyCrypto
-

 Regulation10 months ago
Regulation10 months agoNancy Pelosi Considers Supporting Republican Crypto Bill FIT21 – London Business News
-

 Videos12 months ago
Videos12 months agoCryptocurrency News: Bitcoin, ETH ETF, AI Crypto Rally, AKT, TON & MORE!!
-

 Regulation12 months ago
Regulation12 months agoBitcoin’s future is ‘bleak’ and ripe for regulation, says lead developer
-

 News9 months ago
News9 months agoAave Price Increases Following Whales Accumulation and V3.1 Launch
-

 Regulation9 months ago
Regulation9 months agoSouth Korea Imposes New ‘Monitoring’ Fees on Cryptocurrency Exchanges
-

 Regulation9 months ago
Regulation9 months agoA Blank Sheet for Cryptocurrencies: Kamala Harris’ Regulatory Opportunity
-

 Regulation9 months ago
Regulation9 months agoCryptocurrency Regulations in Slovenia 2024
-

 News12 months ago
News12 months agoThe trader earned $46 million with PEPE after reaching a new ATH
-

 Regulation11 months ago
Regulation11 months agoCrypto needs regulation to thrive: Tyler Cowen
-

 Blockchain11 months ago
Blockchain11 months agoSolana ranks the fastest blockchain in the world, surpassing Ethereum, Polygon ⋆ ZyCrypto
-

 Blockchain11 months ago
Blockchain11 months agoSolana Surpasses Ethereum and Polygon as the Fastest Blockchain ⋆ ZyCrypto

















