Blockchain
Impostazione di un ambiente di sviluppo per Blockchain
1. Introduzione
Blockchain sta guadagnando popolarità e si sta sviluppando oggi grazie alla sua promessa di innovazione e decentralizzazione. Sebbene possa sembrare affascinante dall’esterno, immergersi senza un ambiente ben configurato è altrettanto scoraggiante. Ma non preoccuparti: ci pensiamo noi!! Questo articolo si addentra nella nicchia della blockchain, fornendo guide dettagliate e approfondimenti su misura per gli interessi e le esigenze degli sviluppatori di blockchain. Preparati a esplorare il mondo della blockchain con questo entusiasmante viaggio!!
2. Scegliere gli strumenti giusti
Durante la configurazione del tuo ambiente, è essenziale scegliere gli strumenti giusti in base ai tuoi interessi e requisiti. Di seguito sono riportati gli strumenti e gli editor che puoi esplorare.
Sistema operativo:
È possibile sviluppare applicazioni blockchain su qualsiasi sistema operativo, ma macOS e Linux sono preferibili per una migliore compatibilità e supporto.
Linux: Linux è gratuito e open source e offre flessibilità e personalizzazione. Ha un ampio supporto della comunità e risorse ricche. Ci sono distribuzioni popolari di Linux che sono ampiamente utilizzate. Una è Ubuntu, che è ideale per i principianti, e le altre sono Fedora e Debian. La maggior parte dei progetti di strumenti blockchain sono realizzati con Linux al centro.
Mac OS: MacOS è simile a Linux; è basato su Unix e ha somiglianze nell’esperienza degli strumenti della riga di comando e nell’ambiente di sviluppo. L’integrazione di hardware e software è perfetta. Inoltre, ha un ottimo supporto nativo, come Homebrew, Xcode e Docker.
Finestre: Puoi comunque usare Windows con WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux), questo ti consente di eseguire Linux insieme a Windows. Questo ti dà il meglio di entrambi i mondi, familiarità con Windows e i potenti strumenti di Linux.
Tabella delle differenze tra OS/Mac/Linux
1.Editor di codice/IDE:
Un buon editor di codice o IDE può renderti molto più produttivo. Ecco alcune opzioni a cui pensare:
- Codice VSC: È piuttosto leggero e ha fantastici componenti aggiuntivi per diversi linguaggi di programmazione e framework blockchain.
- IDEA di IntelliJ: Questo è potente e molto utile se si ha a che fare con progetti blockchain Java.
- Testo sublime: È veloce e puoi modificarlo molto. È fantastico se ti piace mantenere le cose semplici.
2.Sistemi di controllo delle versioni:
Il controllo delle versioni è estremamente importante per qualsiasi progetto in cui si stia creando qualcosa. Git, insieme a siti Web come GitHub o GitLab, ti aiuta a gestire bene il tuo codice, a lavorare con altre persone e a tenere d’occhio cosa cambia. Questi strumenti semplificano la gestione della tua base di codice, la collaborazione con altri e il rimanere aggiornati su tutti gli aggiornamenti.
3. Installazione del software essenziale
Linguaggi di programmazione
Ecco i passaggi di installazione per i linguaggi comuni utilizzati nello sviluppo blockchain
JavaScript/TypeScript:
Pitone:
Andare:
Ruggine:
Portare:
Docker aiuta a creare ambienti di sviluppo coerenti.
- Passaggi di installazione per Docker.
4. Framework e strumenti per lo sviluppo di blockchain
Il General Setup comprende vari strumenti e librerie che supportano la blockchain indipendentemente dalla blockchain specifica. Ci sono strumenti come Truffle e Hardhat che forniscono un ambiente di sviluppo completo.
- Hyperledger Fabric: uno speciale sistema blockchain pensato per le grandi aziende.
- Tendermint: uno strumento blockchain veloce che supporta i metodi Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) per concordare le cose.
Containerizzazione e Virtualizzazione:
Docker aiuta a mantenere la configurazione del tuo lavoro uguale su computer diversi. Puoi creare contenitori Docker con tutte le dipendenze di cui hai bisogno, il che semplifica la configurazione e la rimozione delle aree di lavoro.
5. Impostazione di reti blockchain locali
Ecco alcuni strumenti generali utili per gestire ed eseguire la blockchain locale:
Docker Compose: Docker Compose è utilizzato per definire ed eseguire applicazioni Docker multi-contenitore. Utilizza un file docker-compose.yml. Ecco i passaggi di installazione per lo stesso:
Kubernetes: un sistema open source per automatizzare la distribuzione, il ridimensionamento e la gestione di applicazioni containerizzate. Ecco i passaggi di installazione per Kubernetes:
File Yaml:
Distribuisci:
La configurazione del nodo locale è utile per testare la tua applicazione in un ambiente controllato. Ecco i passaggi per la configurazione:
Le macchine virtuali ti aiutano a sperimentare con le tue applicazioni senza influenzare l’ambiente locale. Aggiunge anche un ulteriore livello di astrazione.
6. Sviluppo di contratti intelligenti
Lingue comuni:
- Gli smart contract sono generalmente scritti in Solidity e Rust:
- Solidity: ecco come puoi installare Solidity:
| npm install -g solc solc –versione |
Ruggine:
rustup target aggiungi wasm32-sconosciuto-sconosciuto
Compilatori e linter:
I compilatori e i linter sono gli strumenti utilizzati per scrivere smart contract di alta qualità. I compilatori ti aiutano a compilare il codice in modo da poterlo distribuire ulteriormente sulla blockchain.
Ecco i passaggi per compilare un contratto:
1. Solidità:
| solc –bin –abi –optimize -o build/ IlTuoContratto.sol |
| Crea un file .solhint.json
{ “regole”: { “rientro”: [“error”, 4], “citazioni”: [“error”, “double”] }} |
2. Ruggine:
| Installa Clippy: componente rustup aggiungi clippy
Crea un file Clipy.toml[clippy]warnings_as_errors = vero |
Scrivere contratti intelligenti
Durante la scrittura di uno smart contract dovresti tenere a mente le linee guida e le best practice da seguire:
- Assicurati che il tuo codice sia modulare e riutilizzabile
- Eseguire audit di sicurezza
- Garantire l’efficienza del gas per ridurre i costi di transazione
- Eseguire test approfonditi
- Documenta correttamente il tuo codice
- Utilizzare le librerie SafeMath
- Controllare sempre i valori di ritorno e gli errori
- Evita di codificare i valori nel tuo contratto
- Segui uno stile di codifica coerente
- Implementare meccanismi di controllo degli accessi
- Aggiornare regolarmente le dipendenze
- Utilizzare gli eventi per la registrazione
- Utilizzare le librerie standard.
- Utilizzare portafogli multifirma
- Avere un piano di manutenzione a lungo termine del contratto.
7. Test e debug
Framework di test:
- Il testing è il pilastro finale e più forte di qualsiasi sviluppo. Mocha e Chai sono essenziali per testare i contratti in JavaScript. Mocha è un framework di test e Chai è una libreria di asserzioni, entrambi all’unisono per aiutare nell’esecuzione dei test e nella scrittura di asserzioni di test. Waffle è un framework di test che si integra perfettamente con Hardhat. Fornisce capacità di test avanzate e ha asserzioni complete.
Strumenti di debug:
- Il debugging consiste nel trovare i bug e correggerli nel tuo codice. Alcuni strumenti aiutano in questo. Strumenti come Remix, GDB sono usati per il debug.
Test continuo:
Testare tutto il tempo è estremamente importante quando si crea software oggigiorno. Garantisce che il codice venga controllato e convalidato ripetutamente dalle macchine. Quando si utilizzano strumenti che aiutano con Continuous Integration (CI) e Continuous Deployment (CD), è possibile impostare un sistema che esegue test da solo ogni volta che qualcuno modifica il codice. Ciò aiuta a trovare problemi e mantiene il codice valido.
8. Strumenti di distribuzione
Strategie di distribuzione generali:
- Ecco alcune strategie generali di distribuzione:
- Distribuzione locale: La distribuzione viene eseguita localmente e in modo controllato utilizzando strumenti come Ganache e Docker.
- Distribuzione della rete di prova: Questo viene fatto per testare l’applicazione in un ambiente reale, senza risorse reali.
- Distribuzione della rete principale: Questo è un passaggio cruciale in cui si esegue il deployment sulla rete principale in cui si verificano asset e transazioni reali. Questo deployment richiede test approfonditi prima di essere distribuito.
- Distribuzione automatizzata: Utilizzare pipeline CI/CD per l’implementazione di automazione e ripetizione.
Scripting e automazione:
Ecco come scrivere script per l’automazione:
Script per elmetto:
Utilizzo dei servizi cloud:
L’implementazione di nodi blockchain e smart contract tramite servizi cloud fornisce semplicità, affidabilità e scalabilità. Possiamo utilizzare i seguenti servizi cloud:
Servizi Web di Amazon:
- AWS è un servizio cloud gestito da Amazon, utile per la configurazione di istanze EC2 per l’esecuzione di nodi. Possiamo distribuire contratti intelligenti utilizzando AWS lambda per l’esecuzione senza server.
Azzurro
Azure Blockchain Service ti aiuta a gestire le reti blockchain. Puoi usare Azure Functions o Azure DevOps per mettere in azione la tua blockchain e mantenerla aggiornata.
GCP
Kubernetes Engine (GKE) o Compute Engine di Google Cloud ti consente di configurare nodi blockchain. Google Cloud Functions e Cloud Build semplificano la configurazione della tua blockchain.
9. Connessione a reti esterne
1. Configurazione: Passaggi per la configurazione delle connessioni:
- Configurazione di rete: imposta le configurazioni di rete in base alle tue esigenze. Ecco un esempio di Ethereum:
| File Json: { “reti”: { “rete principale”: { “url”: “https://mainnet.infura.io/v3/IL-TUO-ID-PROGETTO”, “conti”: [“0xYOUR_PRIVATE_KEY”] } }} |
- Variabili d’ambiente: utilizzare file .env e librerie come dotenv per gestire le variabili d’ambiente e archiviare in modo sicuro le informazioni di sicurezza e le chiavi private.
2. API e librerie:
- L’utilizzo di API e librerie per interagire con reti esterne semplifica l’interazione. Ecco alcune API comunemente utilizzate:
| Eteri.js
const { ethers } = require(“eteri”);const provider = new ethers.providers.InfuraProvider(“fattoria”, “IL-TUO-ID-PROGETTO”); |
| Polka.jsconst { ApiPromise, WsProvider } = require(‘@polkadot/api’); const provider = new WsProvider(‘wss://rpc.polkadot.io’); const api = await ApiPromise.create({ provider }); |
| Web3.js per ethereum:
const Web3 = require(‘web3’); const web3 = new Web3(‘https://mainnet.infura.io/v3/ID-TUO-PROGETTO’); |
Integrazione del portafoglio:
- L’integrazione del wallet consente agli utenti di interagire con la blockchain tramite transazioni e interazioni. Ecco i passaggi per l’integrazione del wallet:
Metamaschera:
| const provider = new ethers.providers.Web3Provider(window.ethereum); |
Portafoglio Connect:
| const WalletConnectProvider = require(“@walletconnect/web3-provider”);
const provider = new WalletConnectProvider({ infuraId: “IL-TUO-INFURA-ID” }); |
10. Integrazione e distribuzione continua (CI/CD)
Strumenti CI/CD generali:
- Azioni GitHub: GitHub Actions consente di impostare CI/CD per blockchain.
Interfaccia a riga di comando di Travis:
Circle CLI: CircleCI è un altro modo per fare CI/CD che funziona bene con i progetti blockchain. CircleCI offre opzioni avanzate per far sì che la distribuzione avvenga in autonomia.
Test e distribuzione automatizzati:
- La scrittura di flussi di lavoro per test e distribuzioni automatizzati garantisce la coerenza del codice e favorisce iterazioni rapide.
| Prova: test del casco npx Distribuzione: |
11. Strumenti di sicurezza
La sicurezza è al centro del mondo blockchain, pertanto è essenziale garantire i migliori strumenti di sicurezza.
Pratiche di sicurezza generali:
- Eseguire revisioni regolari del codice
- Avere controlli di accesso precisi per le funzioni pubbliche e private
- Effettuare controlli regolari
Strumenti di analisi statica:
- Gli strumenti di analisi statica sono utili per identificare le vulnerabilità del nostro codice e correggerle. Alcuni strumenti utilizzati per lo stesso scopo sono Mythril e Slither.
Verifiche regolari:
Eseguire audit esterni e interni regolari e risolvere i problemi che si presentano prima che i contratti vengano sfruttati.
12. Buone pratiche
Struttura delle cartelle:
- Mantenere una struttura delle cartelle corretta e pulita per un accesso organizzato e un ambiente ordinato nel progetto.
variabili ambientali
- Utilizzare i file env e le librerie dotenv
- Utilizzare strumenti di gestione dei segreti come AWS Secret Manager o Azure Key Vault.
Documentazione:
La documentazione del codice è importante tanto quanto la scrittura del codice stesso.
- Mantieni un file README appropriato in modo che altri possano comprendere il tuo progetto
- Aggiungere commenti nel codice ove necessario
- Utilizzare le API wiki o di documentazione del progetto.
13. Conclusion
Possiamo concludere dicendo che impostare l’ambiente giusto è più importante della semplice creazione di applicazioni blockchain. L’impostazione dell’ambiente ha una checklist per selezionare gli strumenti giusti per configurare reti locali e distribuire contratti intelligenti. Seguendo i passaggi e le strategie menzionati in questo articolo puoi creare applicazioni efficienti, robuste e sicure. Imparare continuamente e modificare le cose per adattarle alle tue esigenze ti aiuterà a migliorare la tua configurazione e a crescere con essa, tenendoti al passo con i nuovi progressi nella tecnologia blockchain. Buona codifica!!
Blockchain
Bitcoin (BTC) Price Crashes as Donald Trump’s Win Odds Dip
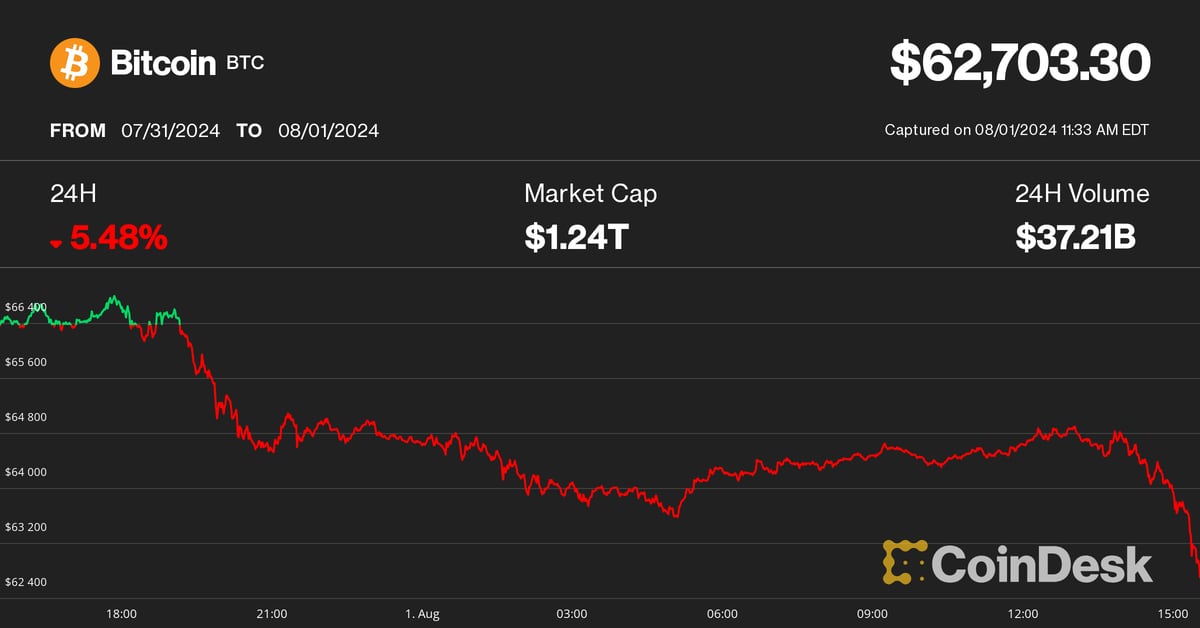
Markets received nominally good news on Thursday morning, with the US ISM manufacturing PMI for July falling much more than economists expected, sending interest rates to multi-month lows across the board. Additionally, initial jobless claims in the US jumped to their highest level in about a year. Taken together, the data adds to the sentiment that the US is on the verge of a cycle of monetary easing by the Federal Reserve, which is typically seen as bullish for risk assets, including bitcoin.
Blockchain
Terra Blockchain Reboots After Reentry Attack Leads to $4M Exploit

Please note that our Privacy Policy, terms of use, cookiesAND do not sell my personal information has been updated.
CoinDesk is a awarded press agency that deals with the cryptocurrency sector. Its journalists respect a rigorous set of editorial policiesIn November 2023, CoinDesk has been acquired from the Bullish group, owner of Bullisha regulated digital asset exchange. Bullish Group is majority owned by Block.one; both companies have interests in a variety of blockchain and digital asset businesses and significant digital asset holdings, including bitcoin. CoinDesk operates as an independent subsidiary with an editorial board to protect journalistic independence. CoinDesk employees, including journalists, are eligible to receive options in the Bullish group as part of their compensation.
Blockchain
$6.8M Stolen, ASTRO Collapses 60%
In the latest news in the blockchain industry, there has been a turn of events that has severely affected Terra and its users and investors, with the company losing $6.8 million. The attack, which exploited a reentry vulnerability in the network’s IBC hooks, raises questions about the security measures of the once celebrated blockchain protocol.
A web3 security company, Cyvers Alerts reported that the exploit occurred on July 31st and caused the company to lose 60 million ASTRO, 3.5 million USDC500,000 USDTand 2. 7 BitcoinThe flaw was discovered in April and allows cybercriminals to make payments non-stop by withdrawing money from the network.
Earth’s response
Subsequently, to the hack employed on the Terra blockchain, its official X platform declared the Suspension network operations for a few hours to apply the emergency measure. Finally in its sendTerra’s official account agreed, sharing that its operations are back online: the core transactions that make up the platform are now possible again.
However, the overall value of the various assets lost in the event was unclear.
Market Impact: ASTRO Crashes!
The hack had an immediate impact on the price of ASTRO, which dropped nearly 60% to $0.0206 following the network shutdown. This sharp decline highlights the vulnerability of token prices to security breaches and the resulting market volatility.
This incident is not the first time Terra has faced serious challenges. Earlier this year, the blockchain encountered significant problems that called into question its long-term viability. These repeated incidents underscore the need for stronger security measures to protect users’ assets and maintain trust in the network.
The recent Terra hack serves as a stark reminder of the ongoing security challenges in the blockchain space. As the platform works to regain stability, the broader crypto community will be watching closely.
Read also: Record Cryptocurrency Theft: Over $1 Billion Stolen in 2024
This is a major setback for Terra. How do you think this will impact the blockchain industry?
Blockchain
Luxembourg proposes updates to blockchain laws | Insights and resources

On July 24, 2024, the Ministry of Finance proposed Blockchain Bill IVwhich will provide greater flexibility and legal certainty for issuers using Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT). The bill will update three of Luxembourg’s financial laws, the Law of 6 April 2013 on dematerialised securitiesTHE Law of 5 April 1993 on the financial sector and the Law of 23 December 1998 establishing a financial sector supervisory commissionThis bill includes the additional option of a supervisory agent role and the inclusion of equity securities in dematerialized form.
DLT and Luxembourg
DLT is increasingly used in the financial and fund management sector in Luxembourg, offering numerous benefits and transforming various aspects of the industry.
Here are some examples:
- Digital Bonds: Luxembourg has seen multiple digital bond issuances via DLT. For example, the European Investment Bank has issued bonds that are registered, transferred and stored via DLT processes. These bonds are governed by Luxembourg law and registered on proprietary DLT platforms.
- Fund Administration: DLT can streamline fund administration processes, offering new opportunities and efficiencies for intermediaries, and can do the following:
- Automate capital calls and distributions using smart contracts,
- Simplify audits and ensure reporting accuracy through transparent and immutable transaction records.
- Warranty Management: Luxembourg-based DLT platforms allow clients to swap ownership of baskets of securities between different collateral pools at precise times.
- Tokenization: DLT is used to tokenize various assets, including real estate and luxury goods, by representing them in a tokenized and fractionalized format on the blockchain. This process can improve the liquidity and accessibility of traditionally illiquid assets.
- Tokenization of investment funds: DLT is being explored for the tokenization of investment funds, which can streamline the supply chain, reduce costs, and enable faster transactions. DLT can automate various elements of the supply chain, reducing the need for reconciliations between entities such as custodians, administrators, and investment managers.
- Issuance, settlement and payment platforms:Market participants are developing trusted networks using DLT technology to serve as a single source of shared truth among participants in financial instrument investment ecosystems.
- Legal framework: Luxembourg has adapted its legal framework to accommodate DLT, recognising the validity and enforceability of DLT-based financial instruments. This includes the following:
- Allow the use of DLT for the issuance of dematerialized securities,
- Recognize DLT for the circulation of securities,
- Enabling financial collateral arrangements on DLT financial instruments.
- Regulatory compliance: DLT can improve transparency in fund share ownership and regulatory compliance, providing fund managers with new opportunities for liquidity management and operational efficiency.
- Financial inclusion: By leveraging DLT, Luxembourg aims to promote greater financial inclusion and participation, potentially creating a more diverse and resilient financial system.
- Governance and ethics:The implementation of DLT can promote higher standards of governance and ethics, contributing to a more sustainable and responsible financial sector.
Luxembourg’s approach to DLT in finance and fund management is characterised by a principle of technology neutrality, recognising that innovative processes and technologies can contribute to improving financial services. This is exemplified by its commitment to creating a compatible legal and regulatory framework.
Short story
Luxembourg has already enacted three major blockchain-related laws, often referred to as Blockchain I, II and III.
Blockchain Law I (2019): This law, passed on March 1, 2019, was one of the first in the EU to recognize blockchain as equivalent to traditional transactions. It allowed the use of DLT for account registration, transfer, and materialization of securities.
Blockchain Law II (2021): Enacted on 22 January 2021, this law strengthened the Luxembourg legal framework on dematerialised securities. It recognised the possibility of using secure electronic registration mechanisms to issue such securities and expanded access for all credit institutions and investment firms.
Blockchain Act III (2023): Also known as Bill 8055, this is the most recent law in the blockchain field and was passed on March 14, 2023. This law has integrated the Luxembourg DLT framework in the following way:
- Update of the Act of 5 August 2005 on provisions relating to financial collateral to enable the use of electronic DLT as collateral on financial instruments registered in securities accounts,
- Implementation of EU Regulation 2022/858 on a pilot scheme for DLT-based market infrastructures (DLT Pilot Regulation),
- Redefining the notion of financial instruments in Law of 5 April 1993 on the financial sector and the Law of 30 May 2018 on financial instruments markets to align with the corresponding European regulations, including MiFID.
The Blockchain III Act strengthened the collateral rules for digital assets and aimed to increase legal certainty by allowing securities accounts on DLT to be pledged, while maintaining the efficient system of the 2005 Act on Financial Collateral Arrangements.
With the Blockchain IV bill, Luxembourg will build on the foundations laid by previous Blockchain laws and aims to consolidate Luxembourg’s position as a leading hub for financial innovation in Europe.
Blockchain Bill IV
The key provisions of the Blockchain IV bill include the following:
- Expanded scope: The bill expands the Luxembourg DLT legal framework to include equity securities in addition to debt securities. This expansion will allow the fund industry and transfer agents to use DLT to manage registers of shares and units, as well as to process fund shares.
- New role of the control agent: The bill introduces the role of a control agent as an alternative to the central account custodian for the issuance of dematerialised securities via DLT. This control agent can be an EU investment firm or a credit institution chosen by the issuer. This new role does not replace the current central account custodian, but, like all other roles, it must be notified to the Commission de Surveillance du Secteur Financier (CSSF), which is designated as the competent supervisory authority. The notification must be submitted two months after the control agent starts its activities.
- Responsibilities of the control agent: The control agent will manage the securities issuance account, verify the consistency between the securities issued and those registered on the DLT network, and supervise the chain of custody of the securities at the account holder and investor level.
- Simplified payment processesThe bill allows issuers to meet payment obligations under securities (such as interest, dividends or repayments) as soon as they have paid the relevant amounts to the paying agent, settlement agent or central account custodian.
- Simplified issuance and reconciliationThe bill simplifies the process of issuing, holding and reconciling dematerialized securities through DLT, eliminating the need for a central custodian to have a second level of custody and allowing securities to be credited directly to the accounts of investors or their delegates.
- Smart Contract Integration:The new processes can be executed using smart contracts with the assistance of the control agent, potentially increasing efficiency and reducing intermediation.
These changes are expected to bring several benefits to the Luxembourg financial sector, including:
- Fund Operations: Greater efficiency and reduced costs by leveraging DLT for the issuance and transfer of fund shares.
- Financial transactions: Greater transparency and security.
- Transparency of the regulatory environment: Increased attractiveness and competitiveness of the Luxembourg financial centre through greater legal clarity and flexibility for issuers and investors using DLT.
- Smart Contracts: Potential for automation of contractual terms, reduction of intermediaries and improvement of transaction traceability through smart contracts.
Blockchain Bill IV is part of Luxembourg’s ongoing strategy to develop a strong digital ecosystem as part of its economy and maintain its status as a leading hub for financial innovation. Luxembourg is positioning itself at the forefront of Europe’s growing digital financial landscape by constantly updating its regulatory framework.
Local regulations, such as Luxembourg law, complement European regulations by providing a more specific legal framework, adapted to local specificities. These local laws, together with European initiatives, aim to improve both the use and the security of projects involving new technologies. They help establish clear standards and promote consumer trust, while promoting innovation and ensuring better protection against potential risks associated with these emerging technologies. Check out our latest posts on these topics and, for more information on this law, blockchain technology and the tokenization mechanism, do not hesitate to contact us.
We are available to discuss any project related to digital finance, cryptocurrencies and disruptive technologies.
This informational piece, which may be considered advertising under the ethics rules of some jurisdictions, is provided with the understanding that it does not constitute the rendering of legal or other professional advice by Goodwin or its attorneys. Past results do not guarantee a similar outcome.
-

 Regulation11 months ago
Regulation11 months agoRipple CTO and Cardano founder clash over XRP’s regulatory challenges ⋆ ZyCrypto
-

 Regulation10 months ago
Regulation10 months agoNancy Pelosi Considers Supporting Republican Crypto Bill FIT21 – London Business News
-

 Videos11 months ago
Videos11 months agoCryptocurrency News: Bitcoin, ETH ETF, AI Crypto Rally, AKT, TON & MORE!!
-

 Regulation11 months ago
Regulation11 months agoBitcoin’s future is ‘bleak’ and ripe for regulation, says lead developer
-

 News8 months ago
News8 months agoAave Price Increases Following Whales Accumulation and V3.1 Launch
-

 Regulation8 months ago
Regulation8 months agoSouth Korea Imposes New ‘Monitoring’ Fees on Cryptocurrency Exchanges
-

 Regulation8 months ago
Regulation8 months agoA Blank Sheet for Cryptocurrencies: Kamala Harris’ Regulatory Opportunity
-

 Regulation8 months ago
Regulation8 months agoCryptocurrency Regulations in Slovenia 2024
-

 News11 months ago
News11 months agoThe trader earned $46 million with PEPE after reaching a new ATH
-

 Regulation10 months ago
Regulation10 months agoCrypto needs regulation to thrive: Tyler Cowen
-

 Blockchain11 months ago
Blockchain11 months agoSolana ranks the fastest blockchain in the world, surpassing Ethereum, Polygon ⋆ ZyCrypto
-

 Blockchain10 months ago
Blockchain10 months agoSolana Surpasses Ethereum and Polygon as the Fastest Blockchain ⋆ ZyCrypto





