Blockchain
Which Statement is True About Blockchain?


-
Blockchain Council
-
July 06, 2024
Blockchain has been a hot topic for a while, sparking conversations and debates worldwide. It’s everywhere, from financial news to tech forums. But with all the buzz, it can be tricky to figure out what’s true and what’s not. Is it just for Bitcoin? Can it really change the way we handle data?
Let’s understand which of the following statements are true about Blockchain and why!
Which Statement is True About Blockchain?
1. Blockchain technology is only used for cryptocurrency transactions.
False. While Blockchain technology gained popularity through cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, it has many other applications. Blockchain enhances transparency and security in various industries such as finance, supply chain management, healthcare, real estate, and more. For example, it helps track and verify products in supply chains, manage medical records securely, and streamline real estate transactions.
2. Blockchain transactions can be easily altered once recorded.
False. One of the main features of Blockchain is its immutability. Once a transaction is recorded on the Blockchain, it cannot be easily altered or deleted. This ensures data integrity and security, making Blockchain a reliable solution for recording and verifying transactions.
3. Blockchain can only operate in a decentralized manner.
False. While decentralization is a key feature of many Blockchain implementations, it is not a strict requirement. Some Blockchain networks operate in a more centralized manner, where a single or limited number of entities control the network. These are often referred to as private or permissioned Blockchains, used by organizations for specific applications like supply chain management or interbank settlements.
4. All Blockchain technologies require extensive energy consumption.
False. The energy consumption of Blockchain technologies varies. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, which use Proof of Work (PoW) consensus algorithms, are known for their high energy usage. However, other Blockchain systems use more energy-efficient consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Stake (PoS) or Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT), which significantly reduce energy consumption. For example, Ethereum’s transition from PoW to PoS has drastically reduced its energy consumption by over 99%.
5. Blockchain applications are currently widespread in mainstream industries.
True. Blockchain applications have expanded into many mainstream industries. In finance, it is used for secure payments and digital identity verification. The supply chain sector benefits from Blockchain for tracking products and ensuring authenticity. Healthcare uses Blockchain for secure patient data management, and real estate leverages it for transparent property transactions. These examples demonstrate Blockchain’s broad applicability beyond just cryptocurrencies.
6. Blockchain technology can enhance the transparency and efficiency of supply chains.
True. Blockchain technology offers significant benefits for supply chain management. It creates an immutable ledger that records every transaction and movement of goods, ensuring data accuracy and security. This allows stakeholders to verify and audit the supply chain in real-time. For example, Walmart uses Blockchain to track the movement of leafy greens, ensuring product safety and traceability. Blockchain helps improve transparency, reduce fraud, and streamline various processes like procurement and payments.
7. Blockchain transactions can be easily reversed or altered once they have been added to the ledger.
False. One of the core features of Blockchain technology is its immutability. Once a transaction is recorded on the Blockchain, it cannot be easily altered or deleted. This ensures the integrity and security of the data, making Blockchain a reliable system for recording transactions. The immutable nature of Blockchain prevents unauthorized changes and tampering.
8. Artificial intelligence can be integrated with Blockchain to improve supply chain management by automating data analysis and optimizing processes.
True. Integrating artificial intelligence (AI) with Blockchain can significantly enhance supply chain management. AI can analyze large volumes of data to optimize processes, predict risks, and improve decision-making. Combined with Blockchain’s transparency and data integrity, AI can automate and streamline supply chain operations, making them more efficient and reliable. For instance, AI can use Blockchain data to optimize inventory management and predict supply chain disruptions.
9. Blockchain applications are expanding into areas beyond cryptocurrencies, such as healthcare and identity verification.
True. Blockchain technology is being used in various sectors beyond cryptocurrencies. In healthcare, Blockchain secures patient data and streamlines the sharing of medical records. For identity verification, Blockchain provides secure and tamper-proof solutions. Other industries, such as real estate, voting systems, and supply chain management, also benefit from Blockchain’s capabilities in enhancing transparency, security, and efficiency.
10. Blockchain technology is only used for financial transactions and has no other practical applications.
False. While Blockchain is well-known for its role in financial transactions and cryptocurrencies, it has numerous other applications. Blockchain enhances transparency and efficiency in supply chains, secures patient data in healthcare, verifies product authenticity in retail, and provides tamper-proof voting systems. These diverse applications show that Blockchain technology has practical uses across many industries, not just finance.
11. Blockchain technology is only used for financial transactions and has no other practical applications.
False. Blockchain technology extends far beyond financial transactions. It enhances transparency and security in supply chains, secures patient data in healthcare, and verifies identities. In real estate, Blockchain streamlines property transactions, and in retail, it helps authenticate products. These diverse applications highlight Blockchain’s versatility across various industries, not just finance.
12. Private Blockchain networks can improve the security of sensitive data but often lack interoperability with other Blockchains.
True. Private Blockchains enhance data security by restricting access to authorized participants. However, they often face interoperability challenges, making it difficult to integrate with other Blockchain networks. This limitation can hinder the seamless exchange of information between different Blockchain systems.
13. All Blockchain platforms are public and allow anyone to participate without restrictions.
False. Not all Blockchain platforms are public. While public Blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum allow open participation, private Blockchains restrict access to authorized users. Additionally, consortium Blockchains involve a group of organizations managing the network together, blending aspects of both public and private Blockchains.
14. Hybrid Blockchains combine elements of both private and public Blockchains, offering both security and transparency where needed.
True. Hybrid Blockchains merge features of both private and public Blockchains. They provide controlled access to sensitive data while maintaining transparency for other information. This combination ensures security and flexibility, making hybrid Blockchains suitable for various applications, such as finance and supply chain management.
15. Consortium Blockchains are ideal for industry groups that need to share data securely among members.
True. Consortium Blockchains, also known as federated Blockchains, are managed by a group of organizations. They balance centralized control with decentralized principles, making them perfect for industry groups that need to share data securely among members. Examples include R3’s Corda, used by financial institutions for secure transactions and data sharing.
Blockchain technology inherently requires significant energy consumption, regardless of the consensus mechanism used.
16. Blockchain as a service (BaaS) is emerging as a significant trend, enabling more companies to utilize Blockchain technology without extensive infrastructure.
True. Blockchain as a Service (BaaS) is gaining traction, allowing businesses to adopt Blockchain technology without the need for extensive infrastructure investments. BaaS providers offer platforms that handle the setup, maintenance, and security of Blockchain networks, enabling companies to focus on their core operations while leveraging Blockchain’s benefits. This trend makes Blockchain accessible to a wider range of organizations, from startups to large enterprises
17. Smart contracts on Blockchain can automate and secure contract fulfillment, reducing the need for manual oversight.
True. Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code. They automatically enforce and execute the contract when predefined conditions are met, reducing the need for intermediaries and manual oversight. This ensures security and transparency, as all actions are recorded on the Blockchain. Industries like finance, real estate, and supply chain management are leveraging smart contracts to streamline operations and reduce costs.
18. Blockchain technology is fully mature and no longer faces significant developmental challenges.
False. While Blockchain has made significant advancements, it still faces developmental challenges. Scalability, interoperability, and regulatory issues are ongoing concerns. Additionally, the integration of new technologies like quantum computing and improvements in energy efficiency are areas of active research and development.
19. In the telecommunications industry, Blockchain is being used to manage mobile roaming transactions and billing.
True. Blockchain is being utilized in telecommunications to enhance the efficiency and transparency of mobile roaming and billing. It enables secure and automated processing of roaming agreements, reducing fraud and operational costs. By using a decentralized ledger, telecom companies can ensure accurate and tamper-proof records of all transactions.
20. Blockchain networks do not provide any means to track the origin or history of transactions.
False. Blockchain inherently provides a transparent and immutable record of all transactions. Each transaction is recorded in a block that is linked to previous blocks, forming a chain. This allows anyone to trace the origin and history of transactions back to their source. This transparency is one of Blockchain’s key features, making it valuable for applications requiring auditability and trust, such as supply chain management and financial transactions.
21. Blockchain can help reduce identity theft by securely storing personal identity information on a decentralized network.
True. Blockchain technology enhances identity security by storing personal information on a decentralized network. This makes it difficult for hackers to access and alter data. Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs) and Verifiable Credentials (VCs) ensure secure and tamper-proof identity verification, giving individuals control over their personal information. This reduces the risk of identity theft and fraud, as only the individual can grant access to their data. Moreover, self-sovereign identity (SSI) frameworks built on Blockchain allow individuals to control and manage their personal information securely, preventing unauthorized access and reducing the risk of identity theft.
22. Private Blockchains provide transparency and are accessible by anyone on the internet.
False. Private Blockchains restrict access to authorized participants only. They enhance privacy and control over data, but they do not provide the same level of transparency as public Blockchains. Only selected members can view and validate transactions, making them suitable for internal business processes rather than open, public access.
23. The integration of Blockchain and IoT can bolster security against hacking and unauthorized data access.
True. Combining Blockchain with the Internet of Things (IoT) enhances security by creating a tamper-proof ledger for IoT devices. Blockchain can securely record and verify the data generated by these devices, reducing the risk of hacking and unauthorized access. This integration ensures that data integrity is maintained across the network, making IoT systems more resilient to attacks.
24. Blockchain can be used to ensure the authenticity and integrity of digital content, including preventing the spread of deep fakes.
True. Blockchain technology can verify the authenticity and integrity of digital content by creating a transparent and immutable record of its creation and modifications. This helps in tracking the origin and history of digital files, making it difficult to alter them without detection. For instance, Blockchain can be used to certify the authenticity of videos, images, and documents, thus helping to combat the spread of deep fakes and other fraudulent content.
25. Blockchain has reached its peak in innovation and no longer drives new technological advancements.
False. Blockchain technology continues to evolve and drive new technological advancements. Innovations such as layer 2 solutions, which reduce energy consumption, the integration of quantum computing, and integration with AI and IoT for enhanced security and efficiency, are just a few examples. Blockchain applications in various sectors, including finance, supply chain, healthcare, and digital identity, are continuously expanding, showing that the technology still has significant room for growth and development.
Conclusion
Throughout this discussion, we’ve tackled some key truths and debunked popular myths surrounding Blockchain technology. The journey through understanding which statement is true about Blockchain shows us that it is much more than just a platform for cryptocurrency transactions. As we’ve seen, it goes beyond cryptocurrencies, offering new possibilities in various fields. Understanding the basics helps us see its potential and future impact. As Blockchain continues to grow, staying informed about its true capabilities and uses is crucial for anyone curious about technology’s future.
Blockchain
Bitcoin (BTC) Price Crashes as Donald Trump’s Win Odds Dip
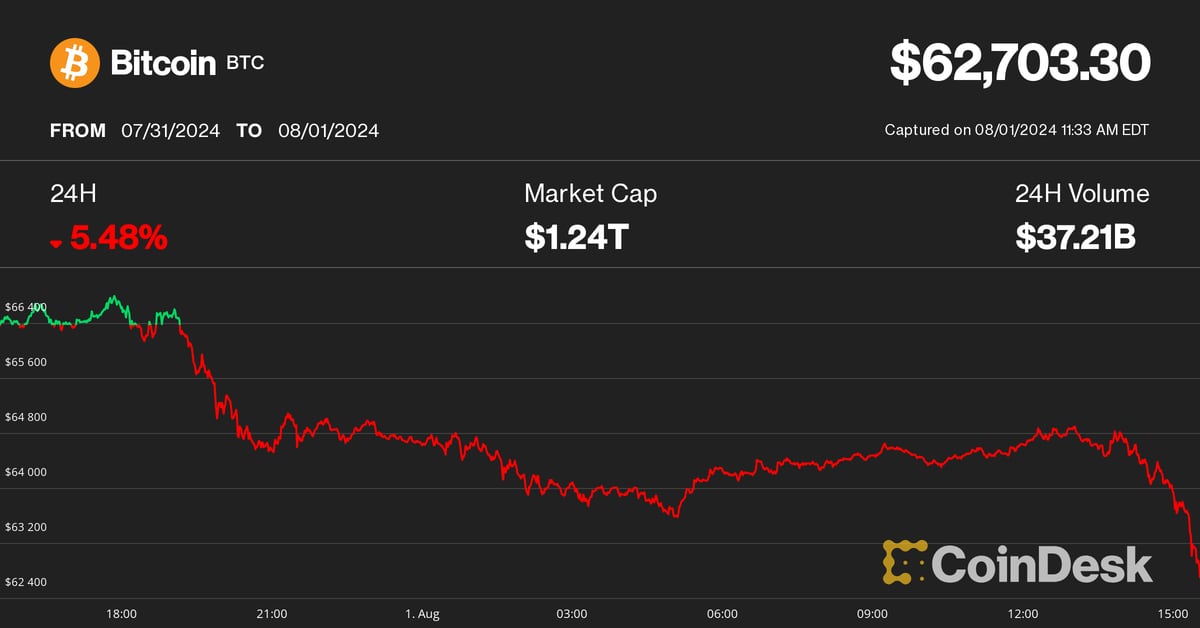
Markets received nominally good news on Thursday morning, with the US ISM manufacturing PMI for July falling much more than economists expected, sending interest rates to multi-month lows across the board. Additionally, initial jobless claims in the US jumped to their highest level in about a year. Taken together, the data adds to the sentiment that the US is on the verge of a cycle of monetary easing by the Federal Reserve, which is typically seen as bullish for risk assets, including bitcoin.
Blockchain
Terra Blockchain Reboots After Reentry Attack Leads to $4M Exploit

Please note that our Privacy Policy, terms of use, cookiesAND do not sell my personal information has been updated.
CoinDesk is a awarded press agency that deals with the cryptocurrency sector. Its journalists respect a rigorous set of editorial policiesIn November 2023, CoinDesk has been acquired from the Bullish group, owner of Bullisha regulated digital asset exchange. Bullish Group is majority owned by Block.one; both companies have interests in a variety of blockchain and digital asset businesses and significant digital asset holdings, including bitcoin. CoinDesk operates as an independent subsidiary with an editorial board to protect journalistic independence. CoinDesk employees, including journalists, are eligible to receive options in the Bullish group as part of their compensation.
Blockchain
$6.8M Stolen, ASTRO Collapses 60%
In the latest news in the blockchain industry, there has been a turn of events that has severely affected Terra and its users and investors, with the company losing $6.8 million. The attack, which exploited a reentry vulnerability in the network’s IBC hooks, raises questions about the security measures of the once celebrated blockchain protocol.
A web3 security company, Cyvers Alerts reported that the exploit occurred on July 31st and caused the company to lose 60 million ASTRO, 3.5 million USDC500,000 USDTand 2. 7 BitcoinThe flaw was discovered in April and allows cybercriminals to make payments non-stop by withdrawing money from the network.
Earth’s response
Subsequently, to the hack employed on the Terra blockchain, its official X platform declared the Suspension network operations for a few hours to apply the emergency measure. Finally in its sendTerra’s official account agreed, sharing that its operations are back online: the core transactions that make up the platform are now possible again.
However, the overall value of the various assets lost in the event was unclear.
Market Impact: ASTRO Crashes!
The hack had an immediate impact on the price of ASTRO, which dropped nearly 60% to $0.0206 following the network shutdown. This sharp decline highlights the vulnerability of token prices to security breaches and the resulting market volatility.
This incident is not the first time Terra has faced serious challenges. Earlier this year, the blockchain encountered significant problems that called into question its long-term viability. These repeated incidents underscore the need for stronger security measures to protect users’ assets and maintain trust in the network.
The recent Terra hack serves as a stark reminder of the ongoing security challenges in the blockchain space. As the platform works to regain stability, the broader crypto community will be watching closely.
Read also: Record Cryptocurrency Theft: Over $1 Billion Stolen in 2024
This is a major setback for Terra. How do you think this will impact the blockchain industry?
Blockchain
Luxembourg proposes updates to blockchain laws | Insights and resources

On July 24, 2024, the Ministry of Finance proposed Blockchain Bill IVwhich will provide greater flexibility and legal certainty for issuers using Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT). The bill will update three of Luxembourg’s financial laws, the Law of 6 April 2013 on dematerialised securitiesTHE Law of 5 April 1993 on the financial sector and the Law of 23 December 1998 establishing a financial sector supervisory commissionThis bill includes the additional option of a supervisory agent role and the inclusion of equity securities in dematerialized form.
DLT and Luxembourg
DLT is increasingly used in the financial and fund management sector in Luxembourg, offering numerous benefits and transforming various aspects of the industry.
Here are some examples:
- Digital Bonds: Luxembourg has seen multiple digital bond issuances via DLT. For example, the European Investment Bank has issued bonds that are registered, transferred and stored via DLT processes. These bonds are governed by Luxembourg law and registered on proprietary DLT platforms.
- Fund Administration: DLT can streamline fund administration processes, offering new opportunities and efficiencies for intermediaries, and can do the following:
- Automate capital calls and distributions using smart contracts,
- Simplify audits and ensure reporting accuracy through transparent and immutable transaction records.
- Warranty Management: Luxembourg-based DLT platforms allow clients to swap ownership of baskets of securities between different collateral pools at precise times.
- Tokenization: DLT is used to tokenize various assets, including real estate and luxury goods, by representing them in a tokenized and fractionalized format on the blockchain. This process can improve the liquidity and accessibility of traditionally illiquid assets.
- Tokenization of investment funds: DLT is being explored for the tokenization of investment funds, which can streamline the supply chain, reduce costs, and enable faster transactions. DLT can automate various elements of the supply chain, reducing the need for reconciliations between entities such as custodians, administrators, and investment managers.
- Issuance, settlement and payment platforms:Market participants are developing trusted networks using DLT technology to serve as a single source of shared truth among participants in financial instrument investment ecosystems.
- Legal framework: Luxembourg has adapted its legal framework to accommodate DLT, recognising the validity and enforceability of DLT-based financial instruments. This includes the following:
- Allow the use of DLT for the issuance of dematerialized securities,
- Recognize DLT for the circulation of securities,
- Enabling financial collateral arrangements on DLT financial instruments.
- Regulatory compliance: DLT can improve transparency in fund share ownership and regulatory compliance, providing fund managers with new opportunities for liquidity management and operational efficiency.
- Financial inclusion: By leveraging DLT, Luxembourg aims to promote greater financial inclusion and participation, potentially creating a more diverse and resilient financial system.
- Governance and ethics:The implementation of DLT can promote higher standards of governance and ethics, contributing to a more sustainable and responsible financial sector.
Luxembourg’s approach to DLT in finance and fund management is characterised by a principle of technology neutrality, recognising that innovative processes and technologies can contribute to improving financial services. This is exemplified by its commitment to creating a compatible legal and regulatory framework.
Short story
Luxembourg has already enacted three major blockchain-related laws, often referred to as Blockchain I, II and III.
Blockchain Law I (2019): This law, passed on March 1, 2019, was one of the first in the EU to recognize blockchain as equivalent to traditional transactions. It allowed the use of DLT for account registration, transfer, and materialization of securities.
Blockchain Law II (2021): Enacted on 22 January 2021, this law strengthened the Luxembourg legal framework on dematerialised securities. It recognised the possibility of using secure electronic registration mechanisms to issue such securities and expanded access for all credit institutions and investment firms.
Blockchain Act III (2023): Also known as Bill 8055, this is the most recent law in the blockchain field and was passed on March 14, 2023. This law has integrated the Luxembourg DLT framework in the following way:
- Update of the Act of 5 August 2005 on provisions relating to financial collateral to enable the use of electronic DLT as collateral on financial instruments registered in securities accounts,
- Implementation of EU Regulation 2022/858 on a pilot scheme for DLT-based market infrastructures (DLT Pilot Regulation),
- Redefining the notion of financial instruments in Law of 5 April 1993 on the financial sector and the Law of 30 May 2018 on financial instruments markets to align with the corresponding European regulations, including MiFID.
The Blockchain III Act strengthened the collateral rules for digital assets and aimed to increase legal certainty by allowing securities accounts on DLT to be pledged, while maintaining the efficient system of the 2005 Act on Financial Collateral Arrangements.
With the Blockchain IV bill, Luxembourg will build on the foundations laid by previous Blockchain laws and aims to consolidate Luxembourg’s position as a leading hub for financial innovation in Europe.
Blockchain Bill IV
The key provisions of the Blockchain IV bill include the following:
- Expanded scope: The bill expands the Luxembourg DLT legal framework to include equity securities in addition to debt securities. This expansion will allow the fund industry and transfer agents to use DLT to manage registers of shares and units, as well as to process fund shares.
- New role of the control agent: The bill introduces the role of a control agent as an alternative to the central account custodian for the issuance of dematerialised securities via DLT. This control agent can be an EU investment firm or a credit institution chosen by the issuer. This new role does not replace the current central account custodian, but, like all other roles, it must be notified to the Commission de Surveillance du Secteur Financier (CSSF), which is designated as the competent supervisory authority. The notification must be submitted two months after the control agent starts its activities.
- Responsibilities of the control agent: The control agent will manage the securities issuance account, verify the consistency between the securities issued and those registered on the DLT network, and supervise the chain of custody of the securities at the account holder and investor level.
- Simplified payment processesThe bill allows issuers to meet payment obligations under securities (such as interest, dividends or repayments) as soon as they have paid the relevant amounts to the paying agent, settlement agent or central account custodian.
- Simplified issuance and reconciliationThe bill simplifies the process of issuing, holding and reconciling dematerialized securities through DLT, eliminating the need for a central custodian to have a second level of custody and allowing securities to be credited directly to the accounts of investors or their delegates.
- Smart Contract Integration:The new processes can be executed using smart contracts with the assistance of the control agent, potentially increasing efficiency and reducing intermediation.
These changes are expected to bring several benefits to the Luxembourg financial sector, including:
- Fund Operations: Greater efficiency and reduced costs by leveraging DLT for the issuance and transfer of fund shares.
- Financial transactions: Greater transparency and security.
- Transparency of the regulatory environment: Increased attractiveness and competitiveness of the Luxembourg financial centre through greater legal clarity and flexibility for issuers and investors using DLT.
- Smart Contracts: Potential for automation of contractual terms, reduction of intermediaries and improvement of transaction traceability through smart contracts.
Blockchain Bill IV is part of Luxembourg’s ongoing strategy to develop a strong digital ecosystem as part of its economy and maintain its status as a leading hub for financial innovation. Luxembourg is positioning itself at the forefront of Europe’s growing digital financial landscape by constantly updating its regulatory framework.
Local regulations, such as Luxembourg law, complement European regulations by providing a more specific legal framework, adapted to local specificities. These local laws, together with European initiatives, aim to improve both the use and the security of projects involving new technologies. They help establish clear standards and promote consumer trust, while promoting innovation and ensuring better protection against potential risks associated with these emerging technologies. Check out our latest posts on these topics and, for more information on this law, blockchain technology and the tokenization mechanism, do not hesitate to contact us.
We are available to discuss any project related to digital finance, cryptocurrencies and disruptive technologies.
This informational piece, which may be considered advertising under the ethics rules of some jurisdictions, is provided with the understanding that it does not constitute the rendering of legal or other professional advice by Goodwin or its attorneys. Past results do not guarantee a similar outcome.
-

 Regulation11 months ago
Regulation11 months agoRipple CTO and Cardano founder clash over XRP’s regulatory challenges ⋆ ZyCrypto
-

 Regulation10 months ago
Regulation10 months agoNancy Pelosi Considers Supporting Republican Crypto Bill FIT21 – London Business News
-

 Videos11 months ago
Videos11 months agoCryptocurrency News: Bitcoin, ETH ETF, AI Crypto Rally, AKT, TON & MORE!!
-

 Regulation11 months ago
Regulation11 months agoBitcoin’s future is ‘bleak’ and ripe for regulation, says lead developer
-

 News8 months ago
News8 months agoAave Price Increases Following Whales Accumulation and V3.1 Launch
-

 Regulation8 months ago
Regulation8 months agoSouth Korea Imposes New ‘Monitoring’ Fees on Cryptocurrency Exchanges
-

 Regulation8 months ago
Regulation8 months agoA Blank Sheet for Cryptocurrencies: Kamala Harris’ Regulatory Opportunity
-

 Regulation8 months ago
Regulation8 months agoCryptocurrency Regulations in Slovenia 2024
-

 News11 months ago
News11 months agoThe trader earned $46 million with PEPE after reaching a new ATH
-

 Regulation10 months ago
Regulation10 months agoCrypto needs regulation to thrive: Tyler Cowen
-

 Blockchain11 months ago
Blockchain11 months agoSolana ranks the fastest blockchain in the world, surpassing Ethereum, Polygon ⋆ ZyCrypto
-

 Blockchain10 months ago
Blockchain10 months agoSolana Surpasses Ethereum and Polygon as the Fastest Blockchain ⋆ ZyCrypto






